Post-natal genetics
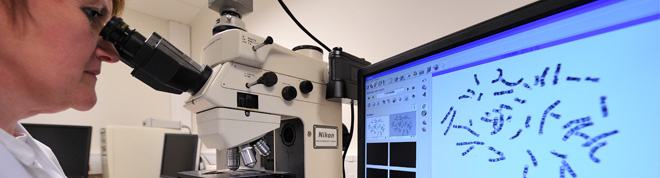
Doctors rely upon post-natal and constitutional genetics in three different situations : the diagnosis of genetics diseases, including pre-symptomatic diagnosis ; the identification of genetic risk factors which could have an impact on a person’s health or determine suitability for treatment ; the detection of healthy carriers in the context of genetic counselling on the risks of transmission to offspring. Post-natal genetic analyses are classified according to two major specialities, each of which require separate authorisations : molecular genetics, which studies a person’s DNA at a molecular level, and cytogenetics, which studies DNA at a chromosomal level.
THE AGENCE DE LA BIOMEDECINE WORKS WITH GENETICS PROFESSIONALS
The Agence leads working groups that bring together cytogenetics and molecular genetics professionals to draft guidelines. The aim is to harmonise practice and improve treatment and the quality of care. In 2010, an agreement was signed with Inserm in the context of Orphanet (a database on rare diseases set up by Inserm) that led to collaboration in the collection of data on post-natal genetics diagnosis activities.
THE ROLE OF THE AGENCE DE LA BIOMÉDECINE
The Agence makes its expertise concerning the geographical organisation of the activities of post-natal diagnosis and genetics available to regional health authorities (agencies empowered to authorise institutions to practise these activities). In this capacity, it expresses an opinion on all requests emanating from cytogenetics laboratories, including molecular cytogenetics laboratories, and molecular genetics laboratories wishing to carry out these activities. In conjunction with the regional health authorities, which perform inspections, it also designs control tools (standards, inspection manuals, control questionnaires, etc.) and takes part in the training of these services.
The Agence accredits practitioners for preimplantation genetic diagnosis and human genetics.
As part of its remit in genetics, the Agence must also provide the general public with information on the use of free-access genetic tests and work with the National Agency for the Safety of Medicines and Health Products (ANSM), to draft a standard that will make it possible to evaluate quality.
Partager